Parkinson’s Disease: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement, balance, and coordination. It occurs when nerve cells in the brain’s substantia nigra begin to malfunction or die, leading to a drop in dopamine levels.
Classification of Parkinson’s Disease
- Type: Chronic, progressive neurodegenerative disorder.
- Classification Explanation: Affects the central nervous system, specifically areas responsible for movement and coordination.
Types of Parkinson’s Disease
- Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: The most common type with no known specific cause.
- Genetic Parkinson’s Disease: Linked to genetic mutations.
- Atypical Parkinsonism: Has similar symptoms but is not true Parkinson’s; includes Multiple System Atrophy and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy.
Health Signs and Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
- Tremors (often in the hands)
- Muscle stiffness
- Slowed movement (bradykinesia)
- Impaired balance and posture
- Speech and writing changes
- Facial masking
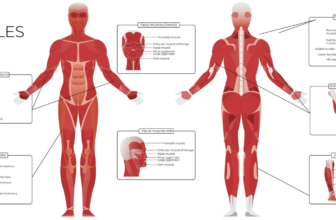
Body Parts Affected by Parkinson’s Disease
- Brain (substantia nigra)
- Muscles
- Nervous system
Parkinson’s Disease Causes
The exact cause is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors, like exposure to toxins, may contribute.
Stages of Parkinson’s Disease
- Early (Stage 1-2): Mild symptoms, often unilateral.
- Intermediate (Stage 3): Balance issues, increased severity in symptoms.
- Advanced (Stage 4-5): Severe disability, possible immobility, dependency on others.
How to Prevent Parkinson’s Disease
While prevention is uncertain, maintaining a healthy lifestyle may reduce risk:
- Regular exercise
- A diet high in antioxidants
- Avoiding toxins
Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosis is primarily clinical and based on symptoms; there is no definitive test.
Testing for Parkinson’s Disease
- Neurological examination
- MRI and CT scans (to rule out other conditions)
- DaTscan (Dopamine Transporter scan) to assess dopamine function
Health Professionals Who Treat Parkinson’s Disease
- Neurologist: Specialized in brain and nervous system disorders.
- Movement Disorder Specialist: Neurologist with expertise in movement disorders.
Reasons to See a Parkinson’s Disease Health Professional
- New or worsening symptoms of tremors, stiffness, or balance issues.
- Diagnosis confirmation or a second opinion.
- Medication or therapy adjustments.
Process to Find the Right Treatment
- Consultation with a neurologist for medication options.
- Physical therapy, occupational therapy, or surgical interventions like Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS).
Preparing to See a Specialist
- Record symptoms, medical history, and medication.
- Note any recent changes in movement, balance, or mood.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- What stage is my condition at?
- What treatment options are available?
- Are there lifestyle changes I should make?
- How can I monitor my symptoms?
- Are there clinical trials for which I qualify?
Types of Treatments for Parkinson’s Disease
- Medications: Levodopa, dopamine agonists, MAO-B inhibitors.
- Surgical Options: Deep Brain Stimulation.
- Therapies: Physical, occupational, and speech therapy.
Health Checkups, Tests, and Examinations
- Regular neurological exams
- Speech and physical assessments
- Mental health screenings
Parkinson’s Disease Clinical Trials
Visit sites like ClinicalTrials.gov for trials on new medications, therapies, and surgical options.
How to Monitor Parkinson’s Disease
- Mobile apps to track symptoms
- Wearable devices for movement and tremor monitoring
Managing Parkinson’s Disease
- Exercise: Improves balance, flexibility, and muscle strength.
- Routine: Establish regular activities and medication schedules.
Caring for Someone with Parkinson’s Disease
- Assist with daily activities and medication management.
- Encourage mobility and social interaction.
- Watch for mental health changes.
Nutrition Dos and Don’ts
- Dos: High fiber, antioxidants, plenty of water.
- Don’ts: Limit processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats.
Lifestyle Dos and Don’ts
- Dos: Regular exercise, mental stimulation, social activities.
- Don’ts: Avoid stress and fatigue; limit alcohol.
Emergency Situations
- Severe falls or injuries
- Sudden loss of movement control
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
Clinical Products for Parkinson’s Disease
- Levodopa: Primary medication to increase dopamine levels.
- Dopamine Agonists: Mimic dopamine effects.
- Mobility Aids: Canes, walkers.
- Wearable Tremor Monitors: Track and analyze tremors.
- Nutritional Supplements: Vitamin D, omega-3s.
Services for Parkinson’s Disease
- Neurologist Consultations: Regular management with specialists.
- Home Care Services: Assistance with daily living.
- Mobile Apps: Symptom tracking and medication reminders.
- Parkinson’s Disease Support Groups: Emotional support and resources.
- Rehabilitation Centers: Physical and occupational therapy.
Questions about Parkinson’s Disease
- What causes Parkinson’s?
- The exact cause is unknown; genetics and environmental factors play roles.
- How is Parkinson’s treated?
- Medications, surgery (DBS), and lifestyle changes.
- Can exercise help Parkinson’s?
- Yes, regular exercise improves symptoms and slows progression.
- What is the life expectancy with Parkinson’s?
- Many live long lives with treatment, though quality of life may decline.
- Is Parkinson’s hereditary?
- Some forms are, but most cases are idiopathic (unknown cause).
- What’s the difference between Parkinson’s and parkinsonism?
- Parkinsonism is a syndrome with similar symptoms but can have other causes.
- Can Parkinson’s be cured?
- There’s currently no cure, but treatments can improve quality of life.
- How do I know if I have Parkinson’s?
- Diagnosis is clinical; consult a neurologist if experiencing symptoms.
- What medications are available?
- Common drugs include Levodopa, MAO-B inhibitors, and dopamine agonists.
- Are there support resources?
- Yes, many support groups and resources are available for patients and caregivers.
The Hosst.com Platform uses a Digital Twin to help users manage their health by tracking, organising, and optimising healthcare activities. It provides personalised insights and assists with scheduling checkups, tests, and doctor visits.
Key features include:
- Symptom management: Recommends tests and treatments based on user input.
- Health data tracking: Monitors glucose, blood pressure, and more from health devices or manual inputs. Connects with your favorite apps and health monitors.
- Alerts: Warns of abnormal health signs and suggests corrective actions.
- Lifestyle recommendations: Offers diet, medication, and lifestyle tips based on health trends.
- Test result interpretation: Simplifies complex results and explains what they mean for the user.
- Preventive care: Sends reminders for checkups and suggests actions to prevent illness.
- Health scenario simulations: Predicts potential health outcomes based on current data.
- Product and service finder: Helps users find the right healthcare product or service.
- Doctor visit preparation: Gathers vitals, history, insurance, and questions for productive visits, with easy sharing to doctors.
- User-friendly: Ask in your own words, available on tablets, desktops, and mobile devices.
The platform simplifies health management and improves well-being. Free and easy to use and no installation required, get started today.
Disclaimer: The information provided in these articles is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions about your health or starting any treatments.
Photo credits Freepik.com