Chronic Pain Comprehensive Guide
What is Chronic Pain?
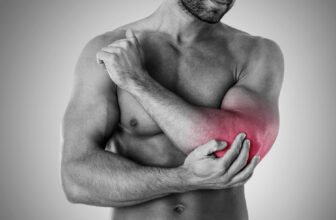
Chronic pain is persistent pain that lasts for more than three to six months, often continuing even after the injury or illness that caused it has healed. It can be a complex, debilitating condition that affects all aspects of a person’s life, including physical, mental, and social well-being.
Classification of Chronic Pain
- Type: Condition.
- Classification Explanation: Chronic pain is considered a long-lasting condition, often associated with a variety of causes and can lead to physical and emotional strain.
Types of Chronic Pain
- Neuropathic Pain: Results from nerve damage or a malfunctioning nervous system, often described as burning or shooting pain.
- Musculoskeletal Pain: Includes pain in muscles, joints, or bones, commonly associated with arthritis, back pain, and injuries.
- Inflammatory Pain: Caused by immune system responses and often seen in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Visceral Pain: Originates from internal organs, often felt as a deep ache or pressure.
- Functional Pain: Pain without an identifiable cause, often associated with conditions like fibromyalgia.
Chronic Pain Health Signs and Symptoms
- Continuous or intermittent pain that persists beyond normal healing
- Muscle stiffness or weakness
- Limited mobility or range of motion
- Sleep disturbances or insomnia
- Mood changes, such as depression or anxiety
- Fatigue and low energy levels
Body Parts Affected by Chronic Pain
Chronic pain can affect virtually any part of the body, but it most commonly impacts the back, neck, head, joints, and muscles. In some cases, chronic pain can be widespread, as seen in fibromyalgia.
Chronic Pain Causes
- Injuries: Trauma or damage from accidents, surgeries, or fractures.
- Diseases: Conditions like arthritis, cancer, and multiple sclerosis can lead to chronic pain.
- Nerve Damage: Injuries or diseases that affect the nervous system.
- Psychological Factors: Stress and emotional factors may exacerbate pain perception.
- Unknown Causes: Some chronic pain conditions, like fibromyalgia, have no clear cause.
Chronic Pain Stages
- Beginner (Acute Phase): Pain begins and may not yet be classified as chronic.
- Medium (Persistent Phase): Pain persists beyond the expected healing period.
- Advanced (Chronic Phase): Pain is established as a chronic condition, often affecting daily activities and mental health.
How to Prevent Chronic Pain
- Regular Exercise: Strengthens muscles and reduces risk of injury.
- Healthy Diet: Anti-inflammatory foods may help reduce pain levels.
- Proper Body Mechanics: Good posture and safe lifting techniques can prevent back pain.
- Stress Management: Reduces the risk of tension and stress-related pain.
- Avoiding Repetitive Movements: Reduces risk of joint and muscle strain.
Chronic Pain Diagnosis
Diagnosis often involves a comprehensive physical exam, assessment of pain history, and evaluation of underlying conditions. Imaging tests, blood tests, and psychological assessments may also be used.
Testing for Chronic Pain
- Physical Examination: Assesses pain location, intensity, and movement restrictions.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, and CT scans help detect structural issues or nerve damage.
- Blood Tests: May reveal inflammatory markers or infection.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: Used for nerve pain to evaluate nerve function.
- Psychological Assessment: Evaluates the impact of pain on mental health.
Health Professionals Who Treat Chronic Pain
- Pain Management Specialists: Physicians focused on pain treatment and management.
- Neurologists: Treat nerve-related pain.
- Orthopedic Specialists: Focus on musculoskeletal pain and injuries.
- Physical Therapists: Help improve mobility and relieve pain through exercises.
- Psychologists: Provide therapy to manage emotional impacts of chronic pain.
Reasons to See a Chronic Pain Health Professional
- Pain persists beyond normal healing time.
- Pain limits daily activities or reduces quality of life.
- Traditional treatments aren’t effective in relieving pain.
- Emotional issues, such as depression or anxiety, are present.
Finding the Right Chronic Pain Treatment
- Consult with a pain specialist for a tailored pain management plan.
- Explore various treatment options like medications, therapy, and physical rehabilitation.
- Seek referrals for multidisciplinary approaches, combining physical and mental health strategies.
Preparing to See a Health Specialist
- Keep a pain diary tracking pain levels, triggers, and treatments tried.
- Prepare a list of questions regarding pain management and treatment options.
- Document any medications or supplements being taken.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- What might be causing my chronic pain?
- What treatment options are available?
- Are there lifestyle changes that could help reduce my pain?
- How can I safely manage my pain with medications?
- What are the risks and benefits of alternative therapies?
Types of Treatments for Chronic Pain
- Medications: NSAIDs, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and opioids (under close supervision).
- Physical Therapy: Strengthens muscles and improves movement.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps manage pain perception and cope with pain.
- Nerve Blocks: Injection treatments for nerve-related pain.
- Complementary Therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic care.
Chronic Pain Checkups, Tests, and Examinations
- Regular pain assessments to monitor changes in pain.
- Imaging scans to monitor any changes in affected areas.
- Psychological evaluations, as pain can have a significant mental health impact.
Chronic Pain Clinical Trials
- New medications for pain relief.
- Experimental non-drug treatments like spinal cord stimulation.
- Research into the effectiveness of alternative therapies, like mindfulness-based interventions.
How to Monitor Chronic Pain
- Pain Apps: Track pain levels, symptoms, and triggers daily.
- Wearable Devices: Monitor physical activity and track inflammation-related metrics.
- Smart Scales: Track weight changes that may impact pain, especially in joints.
Managing Chronic Pain – Living with Chronic Pain
- Develop a routine to avoid pain flare-ups.
- Engage in gentle, regular exercise like yoga or swimming.
- Utilize pain management techniques such as relaxation exercises.
Caring for Someone with Chronic Pain
- Offer emotional support and understanding.
- Assist with daily tasks that may be difficult due to pain.
- Encourage adherence to pain management plans and checkups.
Nutrition Dos and Don’ts
- Dos: Eat anti-inflammatory foods, like fish, nuts, and leafy greens.
- Don’ts: Avoid processed foods and excessive sugar intake, as they may increase inflammation.
Lifestyle Dos and Don’ts
- Dos: Engage in regular low-impact exercise, manage stress, and practice mindfulness.
- Don’ts: Avoid smoking, alcohol, and high-stress activities that can worsen pain.
Emergency Situations
- Sudden and severe increase in pain.
- Pain accompanied by neurological symptoms, like numbness or paralysis.
- Signs of drug overdose if on pain medications (e.g., extreme drowsiness, difficulty breathing).
- Call emergency services if any of these situations arise.
Chronic Pain Clinical Products
- NSAIDs and Acetaminophen: Over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) Units: Provides pain relief through electrical nerve stimulation.
- Pain-Relieving Creams and Patches: Topical options for localized pain.
- CBD Oil: An alternative supplement for pain relief (consult a doctor before use).
- Heating Pads and Ice Packs: Provide localized relief for musculoskeletal pain.
Chronic Pain Services
- Pain Management Clinics: Offer specialized care for managing chronic pain.
- Telemedicine Services: Convenient access to pain specialists for follow-up care.
- Physical Therapy Centers: Assist with mobility and strength to reduce pain.
- Mental Health Therapy: Counseling and therapy to manage the mental impact of chronic pain.
- Health Insurance Support: Helps navigate coverage for pain management treatments and medications.
Top 10 Questions About Chronic Pain
- What is chronic pain?
- Chronic pain is pain lasting more than three months, persisting beyond normal healing.
- Can chronic pain be cured?
- Chronic pain often cannot be cured, but it can be managed effectively.
- What causes chronic pain?
- It can result from injury, disease, nerve damage, or unknown causes.
- Is chronic pain a mental health issue?
- Chronic pain is physical but often affects mental health, requiring both physical and emotional support.
- Can exercise help with chronic pain?
- Yes, gentle exercise can strengthen muscles and reduce pain in many cases.
- Are there non-medication options for pain relief?
- Yes, physical therapy, CBT, acupuncture, and TENS are all alternatives.
- What is the best diet for chronic pain?
- An anti-inflammatory diet focused on whole foods and low in processed items is beneficial.
- How does chronic pain affect sleep?
- Pain can disrupt sleep, leading to a cycle of fatigue and increased pain perception.
- What’s the risk of addiction with pain medications?
- Certain medications like opioids carry a risk; alternatives or close supervision are essential.
- Are there support groups for chronic pain?
- Yes, many communities and online platforms offer chronic pain support groups.
The Hosst.com Platform uses a Digital Twin to help users manage their health by tracking, organising, and optimising healthcare activities. It provides personalised insights and assists with scheduling checkups, tests, and doctor visits.
Key features include:
- Symptom management: Recommends tests and treatments based on user input.
- Health data tracking: Monitors glucose, blood pressure, and more from health devices or manual inputs. Connects with your favorite apps and health monitors.
- Alerts: Warns of abnormal health signs and suggests corrective actions.
- Lifestyle recommendations: Offers diet, medication, and lifestyle tips based on health trends.
- Test result interpretation: Simplifies complex results and explains what they mean for the user.
- Preventive care: Sends reminders for checkups and suggests actions to prevent illness.
- Health scenario simulations: Predicts potential health outcomes based on current data.
- Product and service finder: Helps users find the right healthcare product or service.
- Doctor visit preparation: Gathers vitals, history, insurance, and questions for productive visits, with easy sharing to doctors.
- User-friendly: Ask in your own words, available on tablets, desktops, and mobile devices.
The platform simplifies health management and improves well-being. Free and easy to use and no installation required, get started today.
Disclaimer: The information provided in these articles is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions about your health or starting any treatments.
Photo credits Freepik.com